Protein sequencing technical document
Download our N-terminal protein sequencing technical document below.
Written by our expert technical staff, it provides information on the analysis technique and provides useful information on sample type, preparation and submission.
Related articles
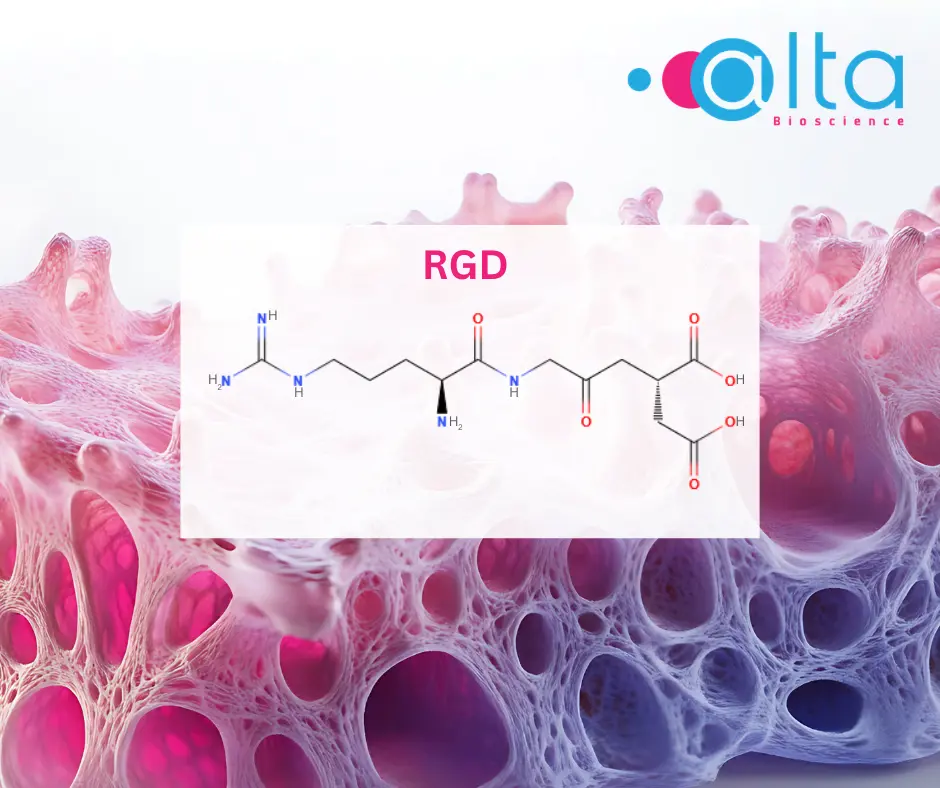
RGD Peptides: Integrin Binding Motifs for Cell Adhesion
Explore RGD peptides, key integrin receptor inhibitors used as tumour homing peptides, and for the functionalisation of inert biomaterial to promote cell adhesion in tissue engineering and 3D cell culture applications.

Peptide PEGylation: Enhancing Therapeutic Performance
Learn more about PEGylated peptides, how they outperform unmodified peptides, and their impact on modern drug development.

How Amino Acids Shape Flavour in Food Products
Discover how amino acids and small peptides shape food flavour through direct taste effects, aroma formation, and product development strategies.
