What are peptides used for?
Peptides, short chains of amino acids, play a crucial role in various biological processes, but what are peptides used for? As fundamental building blocks of proteins, peptides naturally occur in the body and are present in many foods. Beyond their natural functions, synthetic peptides have been harnessed for a diverse range of applications, from medicine and skincare to agriculture and biotechnology. These versatile molecules are crucial in scientific research, biotechnology innovations, and sustainable agricultural practices. Their broad functionality continues to expand as scientists uncover more about their potential.
Medical and pharmaceutical applications
Peptides have revolutionised modern medicine. Synthetic peptides are used to treat several conditions due to their specificity and safety profile. Key medical uses include:
Hormonal therapies
- Insulin: A peptide hormone critical for diabetes management, insulin was the first synthetic peptide developed for therapeutic use.
- Glucagon-like peptides (GLP-1 and GLP-2): These are used to treat type 2 diabetes and short bowel syndrome, respectively, by mimicking natural hormones.
- Peptide hormones such as leptin and ghrelin: For regulating appetite and energy balance
Chronic disease management
- Cardiovascular diseases: Peptides such as angiotensins regulate blood pressure and promote cardiovascular health.
- Autoimmune conditions: Some peptides are used to modulate immune responses in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Cancer immunotherapy: Stimulating the immune system to recognise and attach cancer cells.
- Neurodegenerative disease treatment: Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and other conditions, for example, peptides developed to inhibit amyloid plaque formation
- Parathyroid hormone (PTH): This has been used in the treatment of osteoporosis, promoting bone formation and increasing bone density.
Antimicrobial and antiviral therapies
- Antimicrobial peptides help combat resistant bacterial infections.
- Peptides like bFGF (basic fibroblast growth factor): Used to promote wound healing and tissue regeneration
- Peptide-based drugs like enfuvirtide are vital in HIV treatment.
Gene Therapy
- Peptides are being investigated as delivery agents for gene therapy, facilitating the transport of genetic material into cells. These peptides can help enhance the efficiency of gene-editing tools like CRISPR.
Pain management
- Ziconotide: A peptide derived from marine cone snail venom is used to manage severe chronic pain.
So, what are peptides used for in medicine? They provide groundbreaking solutions in drug development, chronic disease treatment, and beyond. For instance, new developments in peptide research are paving the way for peptide-based cancer immunotherapies, where peptides activate immune cells to target and destroy tumours. Peptide-based drugs are advancing rapidly, with ongoing research into cancer treatments, vaccines, and novel therapeutic applications.
Peptides in skincare and cosmetics
Peptides are highly sought after in the beauty industry for their potential to improve skin health and appearance. They are used in:
- Anti-ageing products: Peptides like collagen stimulate the skin’s natural collagen production, improving elasticity and reducing wrinkles.
- Wound healing: Certain peptides promote skin regeneration and repair damage from ageing or environmental stress.
- Hair care: Peptide-infused serums support thicker, healthier hair growth by nourishing the scalp.
- Cellular repair and regeneration: Peptides like thymosin beta-4 are known for promoting cellular repair and regeneration. These are often used to stimulate wound healing and repair skin damaged by injury, surgery, or chronic conditions.
- Sun protection: Peptides in combination with other ingredients are being explored in sunscreens or after-sun products to offer additional protection against UV damage and support skin recovery from sun exposure.
These benefits make peptides a staple ingredient in high-end moisturisers, serums, and hair products.
Research and biotechnology
Synthetic peptides are indispensable tools in scientific research. They are used to:
- Study protein interactions: Peptides help researchers understand complex biological processes.
- Develop vaccines: Peptide-based vaccines mimic parts of pathogens, stimulating immunity without using live organisms. These vaccines show promise in treating infectious diseases and even cancer.
- Explore drug development: Scientists use peptides to develop new therapies, particularly for diseases involving protein-protein interactions.
- Diagnostics: Peptides are often used in diagnostic tests to detect specific biomarkers, such as in immunoassays (e.g., ELISA). Peptide-based biosensors can help identify disease markers in conditions like cancer, infections, and autoimmune diseases.
- Protein expression and purification: Peptides are frequently used in protein expression systems to produce recombinant proteins in research and biotechnology. They play a crucial role in protein purification, helping researchers isolate specific proteins for study or therapeutic use.
- Antibody production: Peptides are used in the production of monoclonal antibodies, which are critical in research, diagnostics, and treatment of various diseases, including cancers and autoimmune disorders.
- Neuroscience research: Peptides are used to study the function of the brain and nervous system. Neuropeptides help researchers understand neurotransmission, pain pathways, and brain function, aiding in the development of treatments for neurological disorders.
Agricultural and environmental applications
Peptides also have applications in sustainable farming and environmental management:
- Bio-pesticides: Peptides can act as natural, biodegradable pesticides, reducing reliance on chemical alternatives.
- Plant growth regulation: Certain peptides improve crop resilience and growth, ensuring higher yields.
- Soil health: Peptides derived from organic matter help restore nutrient balance in degraded soils.
- Water treatment: Peptides are being investigated as potential agents in water purification. Certain peptides can bind to and remove heavy metals, toxins, and other pollutants from water, providing a sustainable solution for clean water access and environmental remediation.
- Peptide-based feed additives: Used to promote animal growth, improve digestion, and enhance immune function. These peptides help in preventing diseases, reducing the need for antibiotics, and improving overall livestock productivity.
- Bioremediation: Peptides can be used in bioremediation efforts to break down pollutants such as oil spills or pesticides in the environment.
- Climate change mitigation: Peptides are being explored for their role in carbon sequestration by enhancing the ability of plants and soil to absorb and store carbon dioxide.
Dietary supplements and sports nutrition
Peptides are a popular choice for dietary supplements due to their health and fitness benefits:
- Collagen peptides: Known for improving skin elasticity, joint health, and bone density.
- Creatine peptides: These enhance muscle growth and repair, making them popular among athletes.
- Weight management: Some peptides influence metabolism and appetite regulation.
- Immune support: Certain peptides have immunomodulatory properties, helping to support immune function, which is particularly beneficial for athletes who are under intense physical stress and may be more susceptible to illness.
- Hydration: Peptides can aid in hydration and electrolyte balance, with some supplements incorporating peptides to improve the body’s water retention and optimise hydration, which is crucial for athletic performance and recovery.
- Anti-fatigue peptides: Some peptides, like Thymosin Beta-4, are used in supplements for their potential to reduce fatigue and enhance recovery, allowing athletes to perform better and recover faster.
The growing rise of peptides in the nutrition and supplements sector reflects their increasing popularity for supporting muscle recovery, enhancing performance, promoting joint and skin health, and optimising overall wellness.
The future potential of peptides
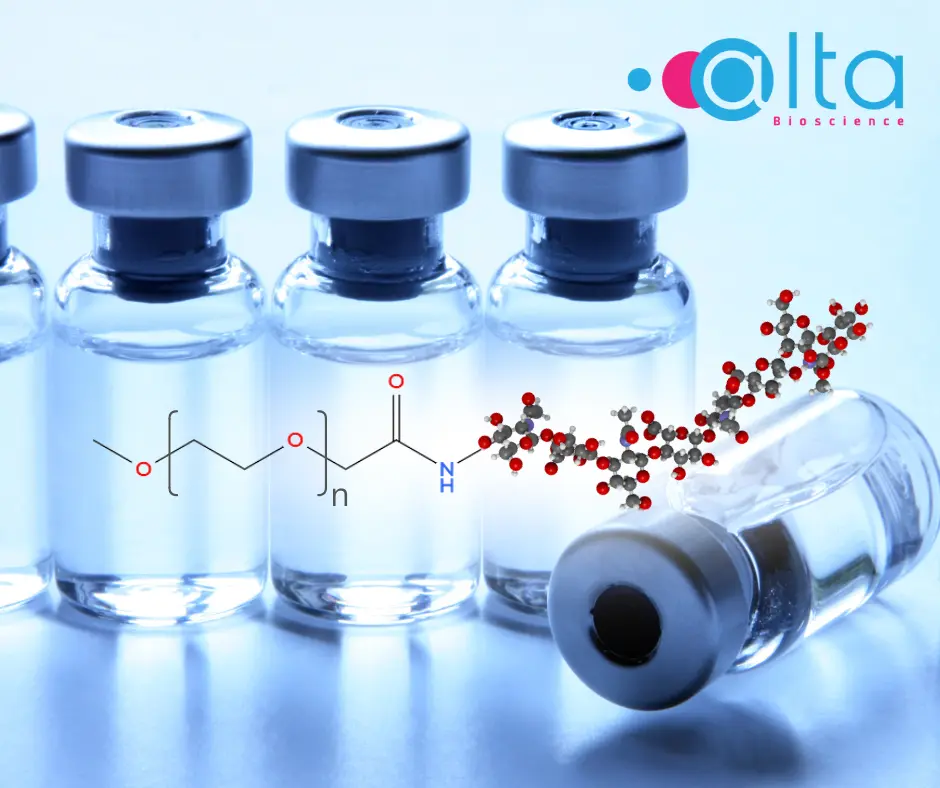
The scope of peptide applications continues to expand. Ongoing research is exploring their use in advanced drug delivery systems, personalised medicine, and even nanotechnology. Beyond their established roles, peptides are being tested for their ability to serve as carriers for precision therapies, such as targeted cancer treatments, which minimise harm to healthy cells while delivering potent drugs directly to diseased tissues. Advances in peptide engineering are also leading to breakthroughs in gene editing, where peptides facilitate the safe delivery of gene-modifying tools. Innovations in peptide synthesis and modification are helping overcome limitations like poor stability and bioavailability, paving the way for even broader uses, including improved vaccine delivery systems and biocompatible materials for medical implants.
Peptides are remarkably versatile molecules with applications spanning medicine, cosmetics, agriculture, and beyond. Their ability to mimic natural biological processes makes them powerful tools in health and science. As research continues, peptides are poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of healthcare, technology, and environmental sustainability. Read more about the fundamentals of peptide synthesis, or talk to us today about our custom peptide synthesis service.